Data from U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that just 6,000 cases of syphilis were reported in the year 2,000. Shockingly, more than 88,000 new cases of syphilis were reported in 2016.
Jessica Shepherd, an ob-gyn in Chicago notes that she has seen the number of these devastating STD infections grow tremendously since 2012.
Statistics from The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services show that syphilis normally affects men who sleep with men, although 10% of new diagnoses are among women.
Syphilis is a super-scary condition, and that’s what makes this alarming news. The bacterial infection is commonly spread through oral, anal, or vaginal sex. It progresses in three different stages. The seemingly prettier face of this condition is it can be easily treated with antibiotics in the first two stages. Nevertheless, if left untreated for 12 months, it becomes latent. This means you may have no symptoms but the bacteria can remain in your body for many years.
The bacteria can become active again after 10 to 30 years. The third stage happens to be the worst. Syphilis can damage your eyes, nerves, heart, and other organs. It can lead to death, permanent blindness, and paralysis.
Shepherd says it is important to go for a diagnosis at an early stage when it can be treated. If untreated during pregnancy, it can be passed on to babies. Most people note they have this venereal disease during the first or second stage. However, some people may not realize their symptoms are a result of the condition.
Related Link:

It is important to be on the lookout for the following symptoms of syphilis.
Swollen lymph glands and fever
A low-grade fever of about 100.4 to 100.6 degrees Fahrenheit can occur at any stage. It can last for a few days or a couple of months. Though fever can be triggered by many things, you should contact your doctor if you suspect syphilis.
Firm and painless sores
Sores that are firm, painless and round can be felt during the first stage of syphilis. They can last three to six weeks. Some people may not notice these multiple sores at the point of infection because they are painless. The sores are slightly larger than a pimple and you can find several in one area. They eventually disappear after some time. Contact your doctor when you notice these sores because if left untreated, the infection advances to the second stage.
Hair loss
You may notice patchy bald spots (syphilitic alopecia) on your scalp during the secondary stages of syphilis. Shepherd notes that this is not a major symptom of syphilis because hair loss can be caused by changes in hormones, medical conditions, and medications. She adds that to suspect syphilis, hair loss should be accompanied by other symptoms like skin rash.
Skin rash
A funky skin rash can occur anywhere during the secondary stage of untreated syphilis. This rash manifests as a small, rough red bump that may disappear unnoticed as it is non-itchy. Most syphilis rashes appear on the soles of your feet or palm of your hands but they are not localized. It is an indication that the bacteria is traveling through your blood and may start affecting other body areas other than where the infection took place.
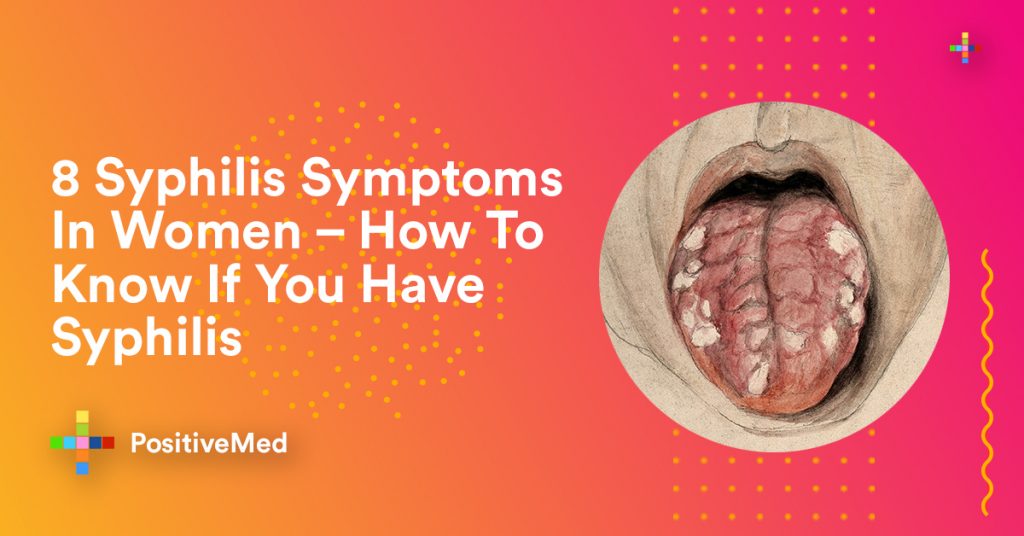
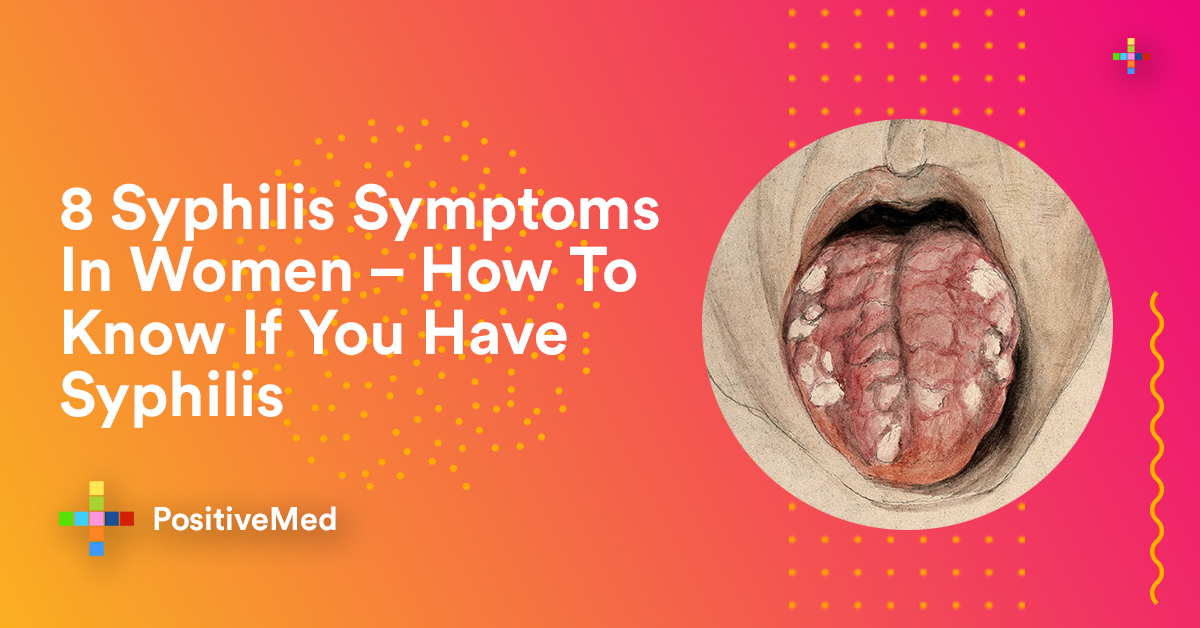
Sores in moist areas
Multiple large gray or white sores can appear on moist skin surfaces including underarm, groin, mouth, anus, or vagina. They may look like genital warts and are also not painful. Shepherd recommends booking an appointment with your ob-gyn if you notice these types of bumps.
Weight loss
Some women lose a couple of pounds during the secondary stage of syphilis. Other symptoms that may accompany weight loss include muscle aches, headaches, fatigue, and sore throat.
Clumsiness and sensory deficits
If untreated, syphilis advances to the tertiary stage whereby it affects the brain. It causes a condition known as neurosyphilis. In reference to the CDC, this condition affects about 10% of patients who fail to seek syphilis treatment at an early stage. It can lead to meningitis, brain damage, or spinal cord inflammation.
Blurred vision
Untreated syphilis can lead to vision impairment or permanent blindness during the tertiary stage. Being a blood-borne pathogen, syphilis can impair the function of any organ including the brain.